How To Draw A Flammability Diagram
Flammability diagram or flammability limerick diagram is one of the of import documents used across the globe to sympathize and prevent fire and explosion. They are mainly used for the hydrocarbon mixture and and then a key to the cargo and send'due south safety on tankers.
It is essential on-board to follow certain procedures based on the studies from the flammability graph of the hydrocarbon mixture.
Flammability diagram explains to us how a gas or mixture of two gases will acquit and take hold of fire with dilution other gas or air.
They are as well sometimes called a ternary diagram every bit it represents flammability range in the mixture of inert gas, oxygen (air), fuel, and nitrogen represented on a triangular diagram.
Burn ( Basics )
Fire safe is the key to the successful operation of industries including shipping. A detailed give-and-take and planning are required on tankers ( A type of transport ) to avoid whatsoever mishap. Proper tank cleaning, loading, and discharging produce to be followed to avert burn down and explosion.
Information technology needs but air, estrus ( source ) and fuel to start a fire. These three components are always available onboard send, and risks are high with tankers.
On tankers fuel is ever present in large quantities in dissimilar holds, the air is nowadays everywhere and the heat source can be from hot piece of work to a spark due to static discharge. removing any side of this burn triangle ( Air, Source, Fuel ) nosotros can forbid burn on-board.
Inert gas is used on-board to remove the one side of the fire triangle i.east air; by pumping in inert gas in tanker holds to go on oxygen level at a minimum. Flammability diagrams are used to understand the tank'due south atmosphere and assistance predicts; how much oxygen to exist maintained at all times.
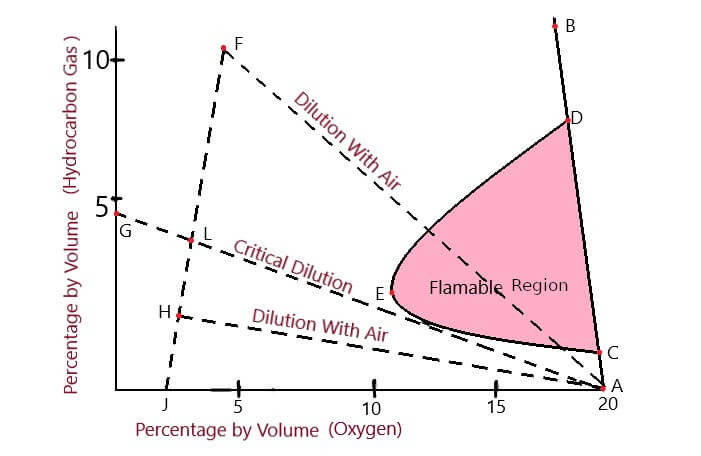
Flammability Diagram
The flammability diagram is the key chemical element for planning prophylactic cargo operation onboard ship. the diagram itself varies for different hydrocarbon gases; and so nosotros must understand how to read and understand information technology.
For example, we go the lower and upper flammability limit of one% to 10% based on the Flammability diagram for rough oil.
Here, line AB represents the mixture of oxygen ( Air ) and particular hydrocarbon gas. Anything that is left to the line AB represents the condition where inert gas is also mixed with the hydrocarbon-air gas mixture.
The gas mixture represented by Air-conditioning on line AB is too lean to catch fire while DB is too rich mixture to get burn.
Now according to the diagram, When we go left to the line AB ( Add inert gas to the tank'due south ) there is a sudden change in tank temper.
Similarly, the upper and lower flammability limits changes with more and more mixing of inert gas. Finally, the upper flammability limit ( The maximum amount of hydrocarbon gas to air mixture which can sustain fire) and lower flammability limit (The minimum amount of hydrocarbon to air gas mixture which can sustain fire ) meet at a point, represented on the diagram as Indicate E.
What is Lean or as well Rich mixture?
In a hydrocarbon-air gas mixture; when it is too rich in fuel to fire is known as a besides-rich mixture. Hither the amount of oxygen required to sustain the fire is absent making it impossible to catch fire. Such an atmosphere can be easily tested on board by using Tankscope.
On another manus when the amount of hydrocarbon-air gas mixture is too lean to catch fire; the mixture is called a lean mixture. On-lath a special equipment called explosimeter is used to detect the presence of hydrocarbon in such an atmosphere.
Understanding Cargo Functioning on Flammability Diagram
Inert gas is pumped into the tanks while and after the successful cargo performance. On the flammability diagram, it can be seen as the decreasing gap between the UFL ( Upper flammability limit ) and LFL ( Lower Flammability limit ). The UFL and LFL encounter at point E; just inert gas is pumped in until information technology reaches to the point F represented on the diagram.
Now during cargo discharge, if the tank atmosphere is diluted with air (Oxygen); information technology will follow a dangerous path FA. From the diagram itself, we can see that the path FA laissez passer through the flammable range and and so can be hazardous. So to avoid such a scenario; inert gas is purged into the tank before and during the cargo operation ( Discharging ).
By purging inert gas into the tanks, Oxygen-Hydrocarbon mixture is taken to bespeak H from F. Now whatsoever further dilution with air while discharging won't cause any risks to the send; as the line HA represented on the flammability diagram don't laissez passer through the flammable range. At present suppose for some reason the tanks are filled with less inert gas than required. Then during discharging information technology will miss the flammable range by a small margin.
On the flammability diagram, it can be seen every bit line GA; which goes almost touching the flammable range. This is chosen the critical dilution; the minimum amount of inert gas required to ensure the hydrocarbon mixture don't become into the range of flammable reason.
Conclusion
Flammability diagrams are an of import certificate used to prevent an explosion onboard ships. An explosion can occur inside the boundaries of the flammable zone in the diagram.
And then it's of import to know and understand the diagram to prevent fire hazards. The flammability diagram shows us that; the presence of inert gas in the cargo holds don't guarantee safe cargo operation.
Unless the corporeality of inert gas is always to a higher place the disquisitional dilution limit. Information technology is well understood that any amount of oxygen below 8% in the hydrocarbon-air gas mixture is not a threat. Only to ensure the proper safety of the ship; it is kept at 5% at all times.
Note: I have tried best to answer your queries. But still, if you have any dubiety; don't forget to comment downwardly below!
Also Read:
- Helpful Guide On Crankcase Explosion | Cause Activeness & Safety
- Listing of Hazards Associated With Petroleum Products
- CO2 Flooding Organisation – Fixed Burn Fighting System Transport
- Oil Tankers In Detail – Types, Sizes, Structure
Or
Request your Topic !

Source: https://shipfever.com/flammability-diagram-explained/
Posted by: mclaughlinfragend.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Draw A Flammability Diagram"
Post a Comment